Pythonda "__slots__" nima?
Python dasturlash tilida har bir class o‘ziga xos atributlarga ega bo‘lishi mumkin. Standart holatda Python obyektning atributlarini saqlash uchun dictionary (dict) ishlatadi. Bu juda qulay, chunki bu xususiyat dasturchiga istalgan vaqt yangi atributlarni dinamik tarzda qo‘shish imkonini beradi.
Lekin, agar kichik va oldindan ma’lum atributlarga ega bo‘lgan class’lar haqida gapiradigan bo‘lsak, dict ko‘p xotira (RAM) olishi mumkin. Chunki Python obyekt yaratishda barcha atributlarni saqlash uchun statik hajmdagi xotirani ajrata olmaydi. Shuning uchun minglab yoki millionlab obyektlar yaratganingizda bu jiddiy muammo tug‘dirishi mumkin.
Ushbu muammoni hal qilish uchun __slots__ dan foydalanish mumkin. __slots__ orqali Pythonga lug‘at(dict) ishlatmaslikni va faqat oldindan belgilangan atributlar uchun xotira ajratishni ko‘rsatish mumkin. Quyida __slots__ ishlatilgan va ishlatilmagan holatlar uchun misol keltirilgan:
__slots__ yo’q holat:
class MyClass:
def __init__(self, name, identifier):
self.name = name
self.identifier = identifier
self.set_up()
# ...
__slots__ bilan:
class MyClass:
__slots__ = ['name', 'identifier']
def __init__(self, name, identifier):
self.name = name
self.identifier = identifier
# ...
2-ko’rsatilgan misol bilan biz xotirani 45–50% gacha ishlatilinishini kamaytirishimiz mumkin. Misol tariqasida bu code’ni o’zingizda ishlatib ko’ring:
import sys
class WithoutSlots:
def __init__(self, a, b):
self.a = a
self.b = b
class WithSlots:
__slots__ = ('a', 'b')
def __init__(self, a, b):
self.a = a
self.b = b
def memory_usage(obj):
size = sys.getsizeof(obj)
if hasattr(obj, '__dict__'):
size += sys.getsizeof(obj.__dict__)
return size
without_slots = WithoutSlots(1, 2)
with_slots = WithSlots(1, 2)
print(f"Memory usage of single instance (WithoutSlots): {memory_usage(without_slots)} bytes")
print(f"Memory usage of single instance (WithSlots): {memory_usage(with_slots)} bytes")
instances = 10**6
print(f"Creating {instances} instances of each class...")
without_slots_instances = [WithoutSlots(i, i + 1) for i in range(instances)]
with_slots_instances = [WithSlots(i, i + 1) for i in range(instances)]
total_without_slots = sum(memory_usage(obj) for obj in without_slots_instances)
total_with_slots = sum(memory_usage(obj) for obj in with_slots_instances)
print(f"Total memory usage (WithoutSlots): {total_without_slots // (1024 * 1024)} MB")
print(f"Total memory usage (WithSlots): {total_with_slots // (1024 * 1024)} MB")
Natija:
Memory usage of single instance (WithoutSlots): 344 bytes
Memory usage of single instance (WithSlots): 48 bytes
Creating 1000000 instances of each class...
Total memory usage (WithoutSlots): 129 MB
Total memory usage (WithSlots): 45 MB
Kamchiliklari:
Endi bizni class’da
__dict__yoki__weakref__bo’lmasligi.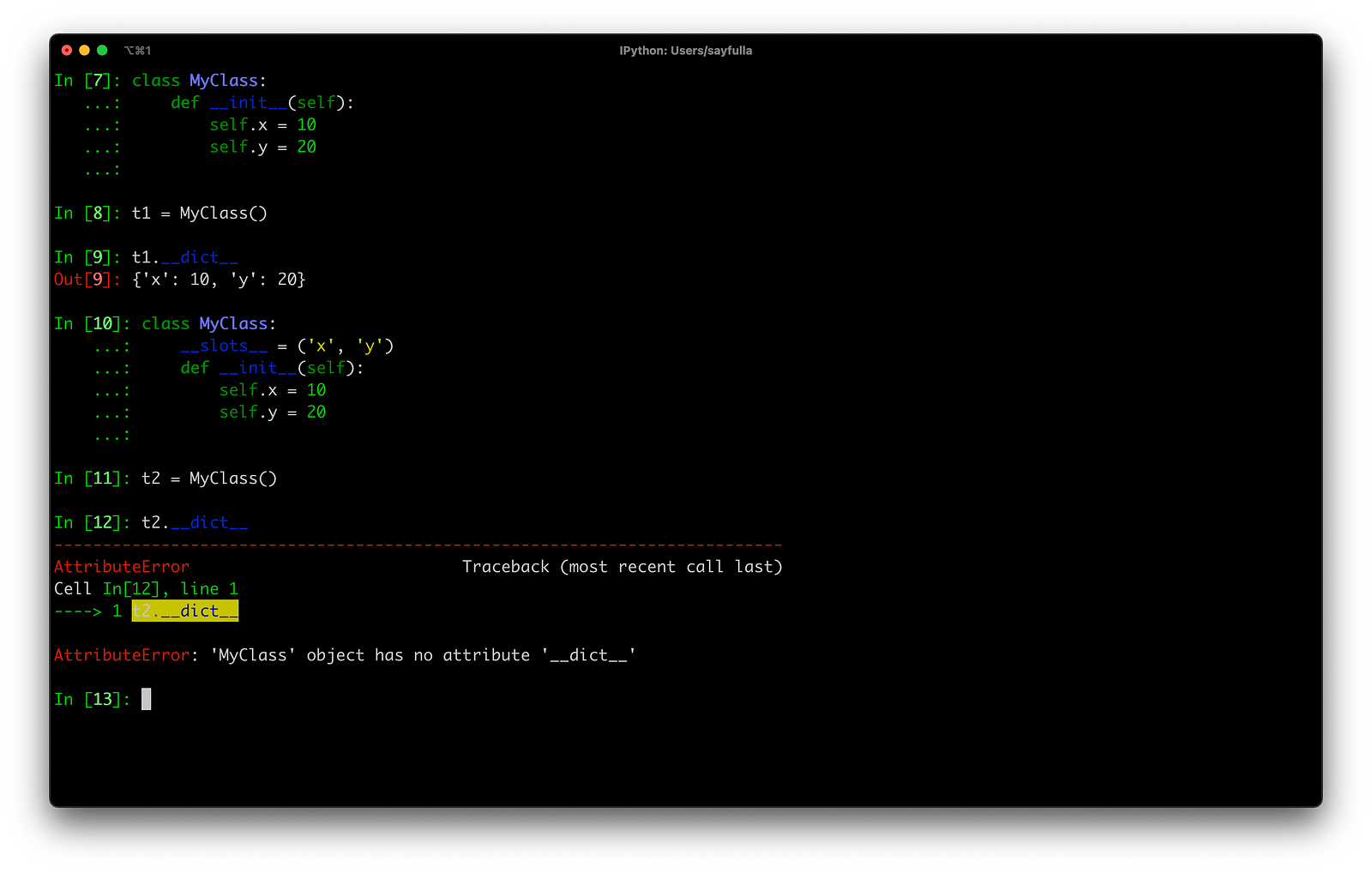
Subclass yaratish endi qiyinroq amalga oshishi mumkin, chunki har bir class uchun
__slots__yozishga to’g’ri kelishi mumkin.
class Base:
__slots__ = ('a',)
class Sub(Base):
__slots__ = ('b',)
Buni hohlamasangiz o’zingiz metaclass yozib qo’ysangiz ham bo’ladi.
Source: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56579348/how-can-i-force-subclasses-to-have-slots
Kanalga obuna bo’ling: https://t.me/sayfulla_notes